Introduction to Data Science¶
Data science¶
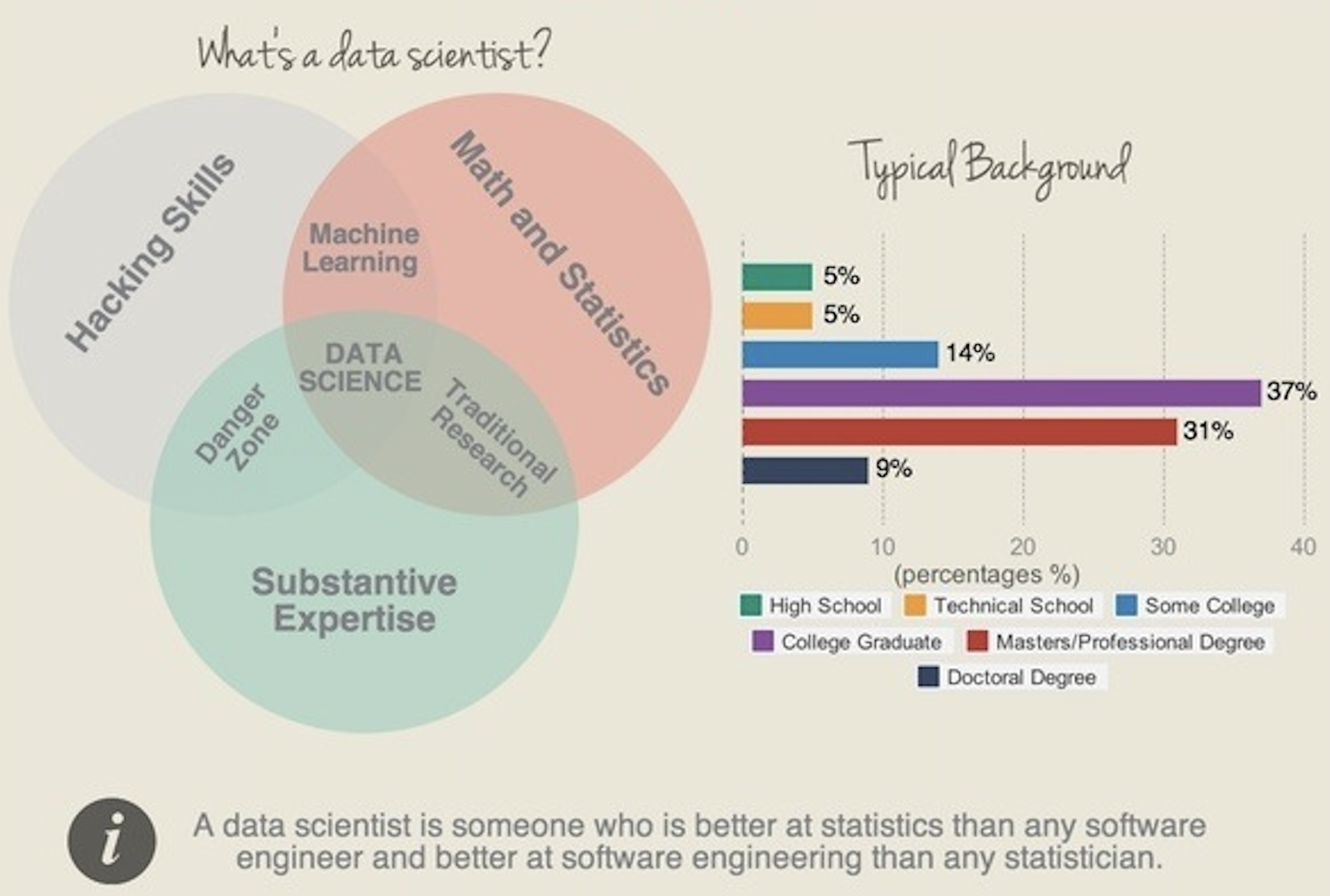
Data science, the science of data analysis, is the applied mathematics in the 21st century.
Source: DataCamp.
Data is increasing in volume, variety, velocity, veracity, and value (5V).
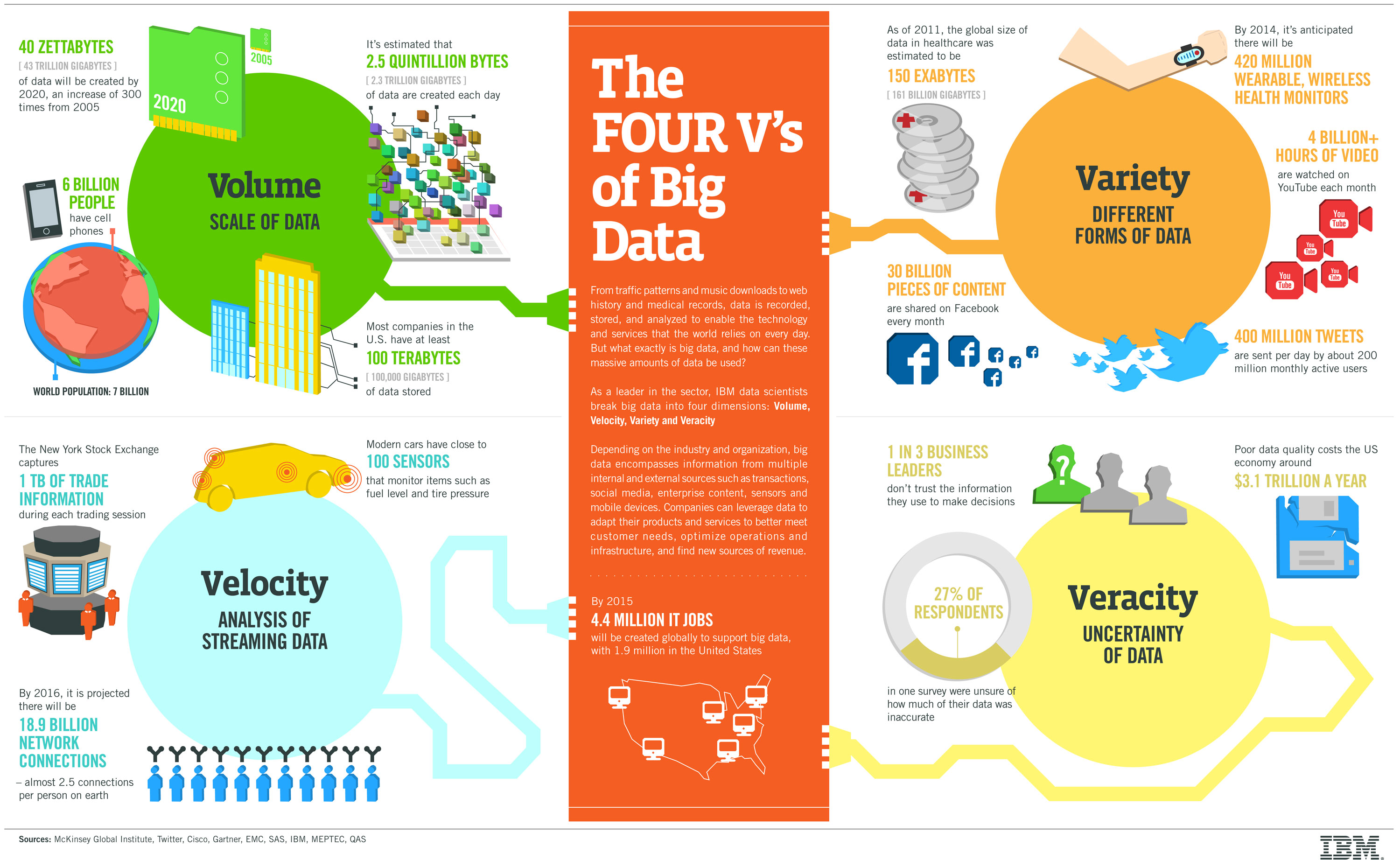
Source: IBM.
My favorite definition of a data scientist (Josh Willis on Twitter?):
A data scientist is someone who is better at statistics than any software engineer and better at software engineering than any statistician.
- Glassdoor consistently ranks data scientists as the top 3 best jobs in America.
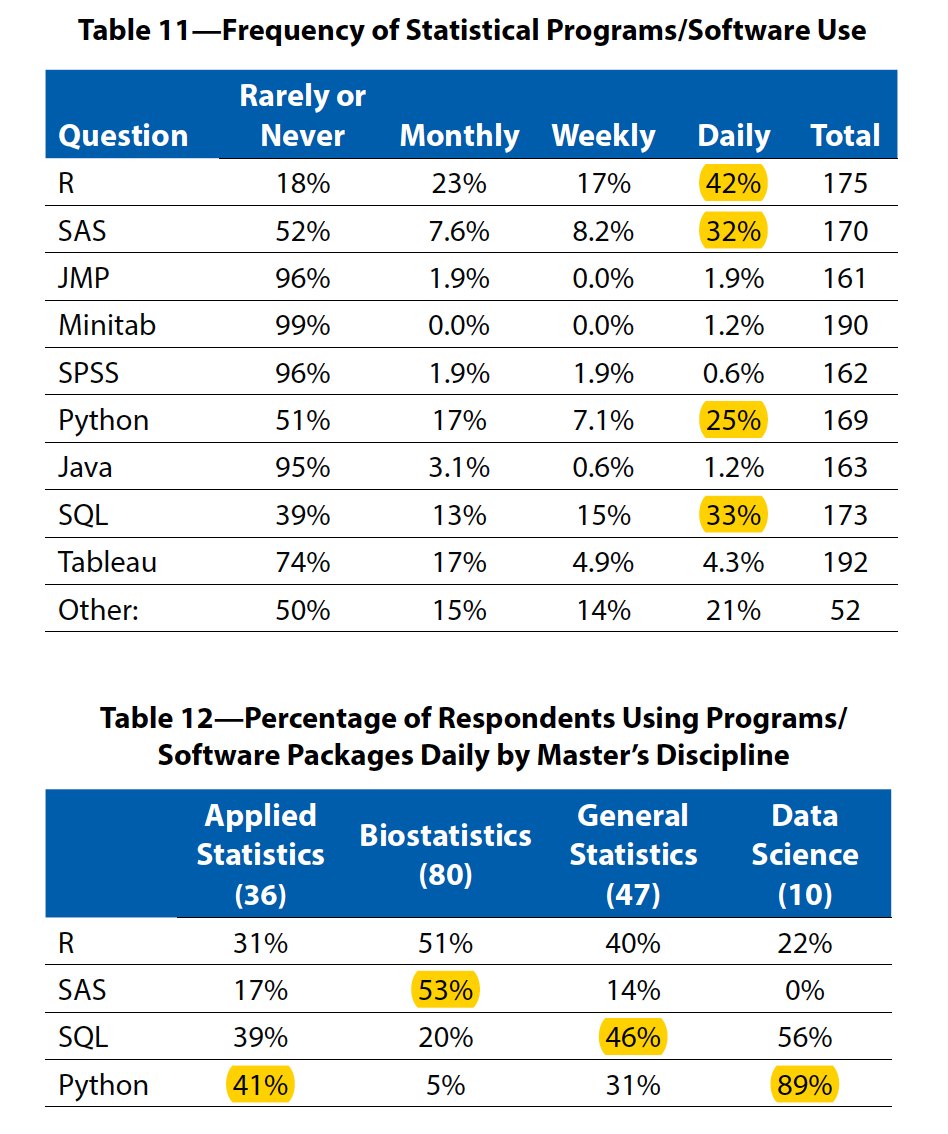
Who are hiring?¶
Following tables are based on a survey of 403 students who earned a master’s degree in statistics, biostatistics, or a related field (actuarial science, data science, informatics, math with stats focus) during the 2019–2020 academic year.
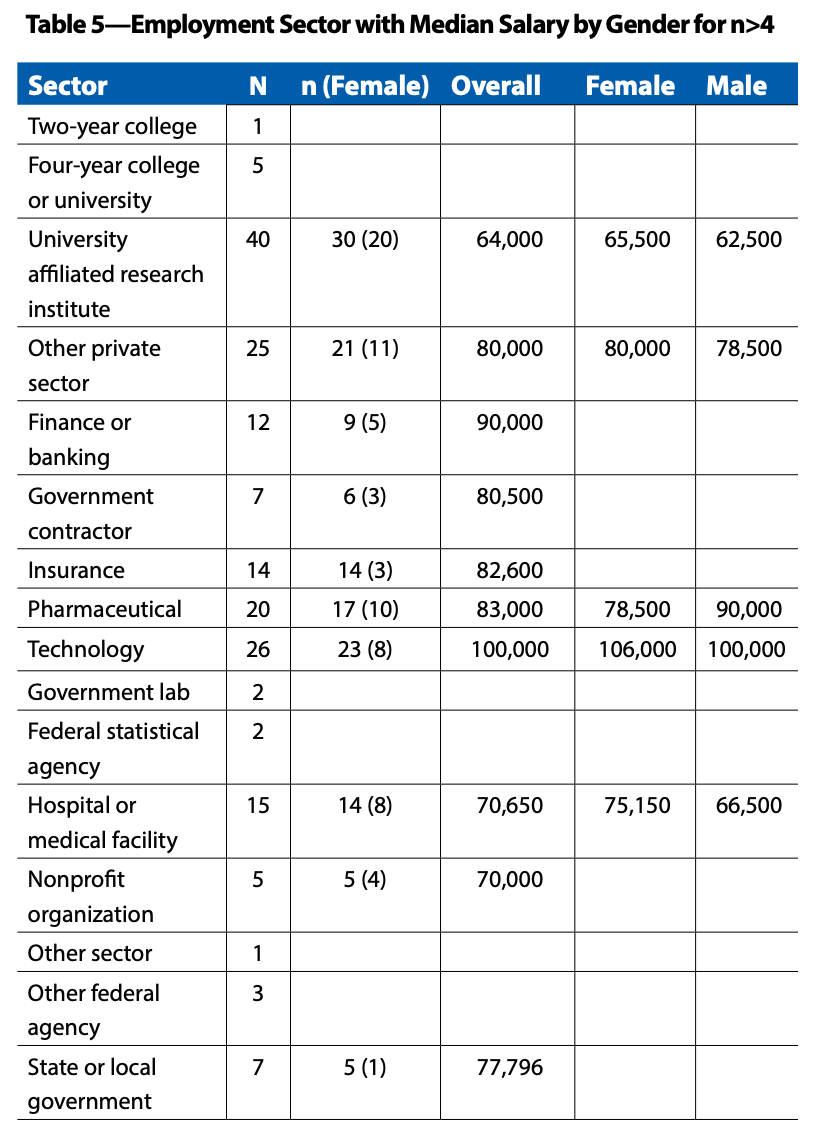
Source: AmStat News (2021 Nov).
there were more than 109 unique—although similar—job titles. The most common were data scientist (20), biostatistician (18), data analyst (9), biostatistician I (7), and statistician (5).
What's this workshop about?¶
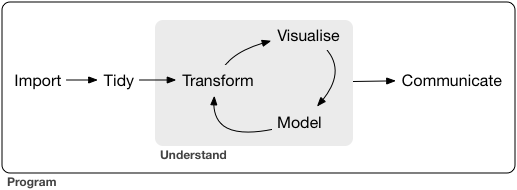
Source: R for Data Science.
- Hands-on experience on a typical data science workflow using Julia, Python, and R.
data ingestion (from text files or databases) -> data wrangling (filtering, selecting, merging, pivoting) -> data visualization (static, interactive) -> data analytics
Module 1 practices the workflow starting from text files.
Module 2 practices the workflow starting from genomic data.
The point is not to memorize all the commands, but to have a high-level understanding of the workflow and appreciate the ease of data manipulations using these languages.
MIMIC data¶

Source: URL
Tutorials in Module 1 use MIMIC IV, an intensive care electronic health record (EHR) dataset curated from over 40,000 patients in the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) at Boston.
Suppose you are the chief data scientist at BIDMC and are tasked developing a predictive model to improve the 30-day mortality rate, a key factor when ranking hospitals.
Given the basic characteristics (e.g., demographics), vital signs, and initial lab tests of a newly admitted ICU patient, can we predict the chance the patient dies within 30 days of the admission?
How to create a meaningful cohort for this predictive modeling?
How to get started¶
Follow instructions at workshop website.